Experiment GPS sync
1 GPS sync
To prove that GPS has been synchronized to the Lidar:
Unplugged GPS and re-power Lidar, config “use_lidar_time=True” –> Factory time
Change the ros system time to a wrong one, config “use_lidar_time=False” –> wrong ros system time
Plug the GPS and “use_lidar_time=True” –> UTC time –> current Time zone time
2 No sync Experiments
Introduction
Two GPS time synchronized Lidars running on a same network with different conditions
Conditions include: (1) different distance of the “roscore” running laptop to the router (2) Whether there is any metal block in between.
The purpose is to find out how long is the time delay causing by the network.
Scenarios
06: has a iron block in between (1m away from both device)
47: has a iron block in between (1m away from both device)
53: no block in between (1m away from both device)
15: closer to rslidar
39: in the middle
12: closer to the new_lidar
Results
bag name |
seq_new |
seq_rc |
data_num |
time_new |
time_rc |
time_diff |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
06 |
87 / 85 |
secs: 1669962265 nsecs: 701245546 |
secs: 1669962265 nsecs: 499892712 |
201 ms |
||
47 |
1324 - 1412 |
681 - 764 |
88 / 83 |
secs: 1669949240 nsecs: 601235390 |
secs: 1669949240 nsecs: 199899912 |
401 ms |
53 |
5048 - 5114 |
4404 - 4469 |
66 / 65 |
secs: 1669949610 nsecs: 801247358 |
secs: 1669949610 nsecs: 699885368 |
101 ms |
15 |
176 - 245 |
112 - 172 |
69 / 60 |
secs: 1669950926 nsecs: 601255178 |
secs: 1669950926 nsecs: 499899149 |
101 ms |
39 |
424 - 480 |
353 - 408 |
56 / 55 |
secs: 1669950950 nsecs: 101251364 |
secs: 1669950950 nsecs: 99894285 |
1.357 ms |
12 |
1349 - 1453 |
1277 - 1381 |
104 / 104 |
secs: 1669951047 nsecs: 401258230 |
secs: 1669951047 nsecs: 399894476 |
1.3637 ms |
New experiment
Roscore running on laptop2 and laptop1 (time delay effect on computer performance)
Add more condition to the experiments: >5m
Conducted time delay experiments, but this time, (ego) “roscore” running on different laptop with different conditions, doesn’t finish the statistical analysis yet.
Two lidars are connected to two different laptops and communicate in a local WIFI network:
laptop1_core/exp6: 06/ 26 / 24 : has a iron block in between (1m away from both device)
laptop2_core/exp1: 37/49/10 : has a iron block in between (1m away from both device)
laptop2_core/exp2: 16/29/39 : no iron block in between, sometimes has people in between (4.06m away from both device)
laptop1_core/exp7: 46/54/04 : no iron block in between, sometimes has people in between (4.06m away from both device)
laptop1_core/exp8: 15/28/39 : no iron block in between (5.22 m away from both device)
laptop2_core/exp3: 25/53/06 : no iron block in between (5.22 m away from both device)
laptop2_core/exp4: 27/46/03 : no iron block in between (1.98 m away from both device)
laptop1_core/exp9: 16/34/45 : no iron block in between (1.98 m away from both device)
Results
exp |
bag_name |
seq_num (new/rs) |
time_new |
time_rs |
time_diff |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
laptop1_exp6 |
26 |
72 / 64 |
secs: 1670053055 nsecs: 801252842 |
secs: 1670053055 nsecs: 799894810 |
1.35 ms |
1m with block |
24 |
73 / 68 |
secs: 1670053113 nsecs: 401238680 |
secs: 1670053113 nsecs: 399894953 |
1.34 ms |
laptop2_exp1 |
37 |
46 / 56 |
secs: 1670053661 nsecs: 101253986 |
secs: 1670053661 nsecs: 199885845 |
-98.63 ms |
1m with block |
49 |
65 / 69 |
secs: 1670053674 nsecs: 1245975 |
secs: 1670053674 nsecs: 99899769 |
- 98. 65 ms |
10 |
57 / 65 |
secs: 1670053694 |
secs: 1670053694 |
-98.63 ms |
|
laptop1_exp7 |
46 |
49 / 48 |
secs: 1670279159 |
secs: 1670279159 |
1.34 ms |
4m |
54 |
65 / 59 |
secs: 1670279168 |
secs: 1670279168 |
1.35 ms |
04 |
81 / 79 |
secs: 1670279180 |
secs: 1670279180 |
101.33 ms |
|
laptop2_exp2 |
16 |
65 / 71 |
secs: 1670278403 nsecs: 101235390 |
secs: 1670278403 nsecs: 99905014 |
1.33 ms |
4m |
29 |
70 / 71 |
secs: 1670278415 |
secs: 1670278415 |
-98.61 ms |
39 |
71 / 77 |
secs: 1670278426 |
secs: 1670278426 |
-98.68 ms |
|
laptop1_exp8 |
15 |
74 / 66 |
secs: 1670280143 |
secs: 1670280143 |
201.33 ms |
5m |
28 |
80 / 78 |
secs: 1670280157 |
secs: 1670280157 |
101.33 ms |
39 |
73 / 67 |
secs: 1670280167 |
secs: 1670280167 |
1.34 ms |
|
laptop2_exp3 |
25 |
64 / 66 |
secs: 1670280991 |
secs: 1670280991 |
-98.65 ms |
5m |
53 |
85 / 92 |
secs: 1670281022 |
secs: 1670281022 |
- 98.63 ms |
06 |
122 / 128 |
secs: 1670281038 |
secs: 1670281038 |
-198.64 ms |
|
laptop1_exp9 |
16 |
97 / 90 |
secs: 1670283386 |
secs: 1670283386 |
101.35 ms |
34 |
- |
- |
- |
- |
|
45 |
135 / 130 |
secs: 1670283419 |
secs: 1670283419 |
101.35 ms |
|
laptop2_exp4 |
27 |
71 / 73 |
secs: 1670283093 |
secs: 1670283093 |
-98.64 ms |
3 Sync_experiments
Introduction
Two GPS time synchronized Lidars running on a same network with the time synchronize algorithms
Also under different conditions
The purpose is to find out:
What happen after running the time synchronization algorithm
The principle of time synchronization algorithm
Results
Here are some statistic results:
bag |
seq_new_o |
seq_rc |
time_diff_ori |
seq_new |
seq_rc |
time_new |
time_rc |
time_diff_syn |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
06 |
87 |
85 |
201 ms |
84 |
84 |
secs: 1669962265 nsecs: 301241636 |
secs: 1669962265 nsecs: 299892664 |
1.3489 ms |
47 |
88 |
83 |
401 ms |
82 |
82 |
secs: 1669949240 nsecs: 101237535 |
secs: 1669949240 nsecs: 99898100 |
1.3394 ms |
53 |
66 |
65 |
101 ms |
64 |
64 |
secs: 1669949610 nsecs: 601249218 |
secs: 1669949610 nsecs: 599889278 |
1.3599 ms |
15 |
69 |
60 |
101 ms |
59 |
59 |
secs: 1669950926 nsecs: 401255369 |
secs: 1669950926 nsecs: 399897099 |
1.35827 ms |
39 |
56 |
55 |
1.357 ms |
54 |
54 |
secs: 1669950949 nsecs: 901249409 |
secs: 1669950949 nsecs: 899892330 |
1.357079 ms |
12 |
104 |
104 |
1.3637 ms |
103 |
103 |
secs: 1669951047 nsecs: 301250219 |
secs: 1669951047 nsecs: 299892426 |
1.35779 ms |
Synchronization always get rid of the last data
4 Principle of synchronization
How time synchronization algorithm works:
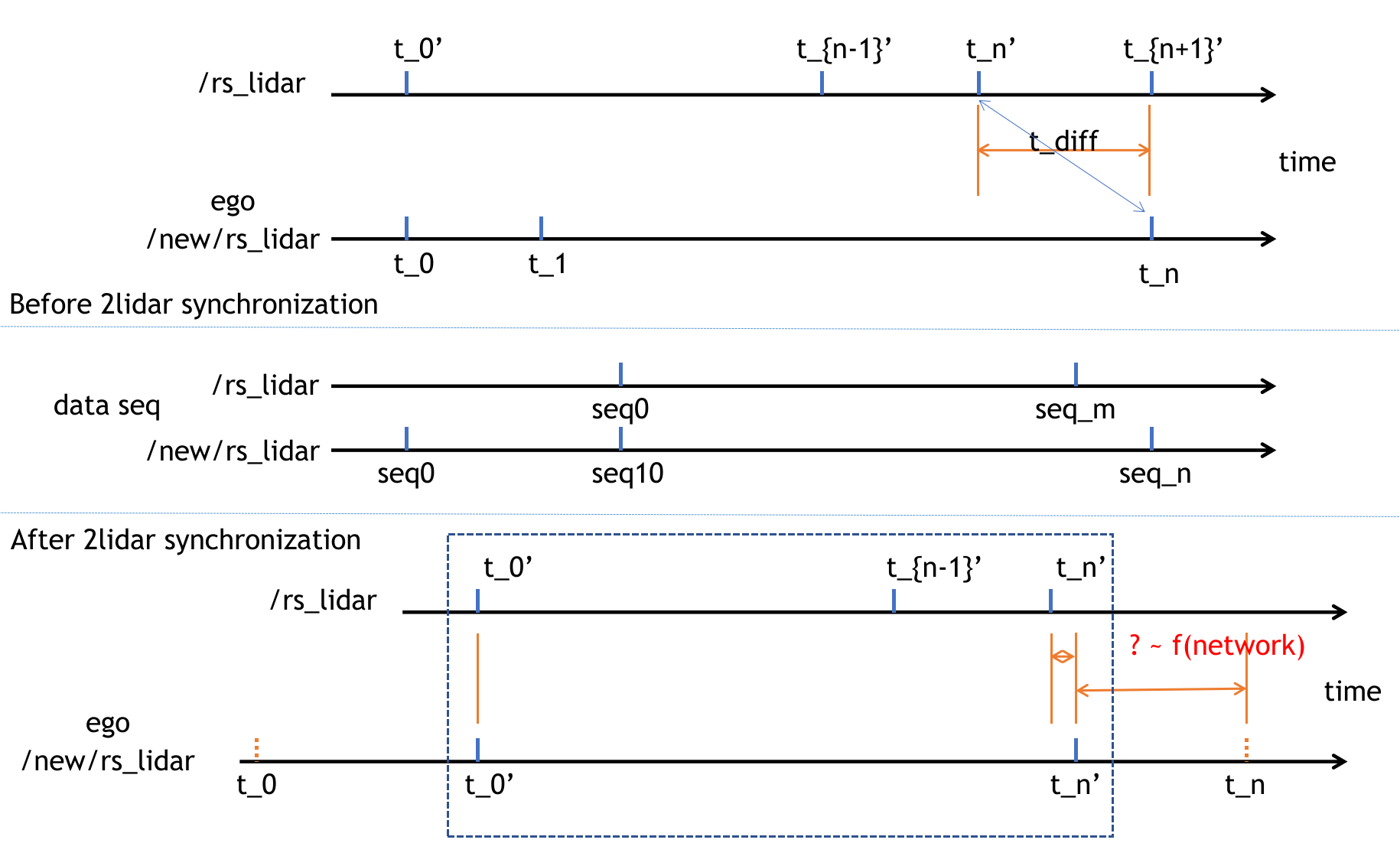
5 Prediction time experiment
Conducting experiments to find out the missing time between two lidars after lidar level time synchronization (red question mark in the previous picture) in terms of network condition (in terms of distance & data throughput)
Results
distance VS. t_predict:
distance |
t_predict |
|---|---|
1m with block |
1.35 ms ~ 400 ms |
- 98. 65 ms |
|
2m |
101.35 ms |
-98.64 ms |
|
4m |
1.35 ms ~ 101.33 ms |
-98.68 ms |
|
5m |
1.34 ms ~ 201.33 ms |
- 98.63 ~ -198.64 ms |
Conclusion:
t_predict does has some relationship with distance: \(t_{predict} = f(distance)\)
However, the
6 Data throughput experiment
Experiment 1
Goals:
Verify the relationship between data throughput vs. time delay
TODO:
Truncate some data from the raw point cloud data, like send only quarter or half raw point cloud.
Note
For this experiment, in order to emphasize the time difference, I put the router in another room.
Results
name |
t_all |
data_num(new/rs) |
time_new |
time_rs |
t_diff |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
laptop1_core1/full_data |
18.4s |
181 / 171 = 10 |
secs: 1670361688 |
secs: 1670361688 |
901.35 ms |
laptop1_core1/three_q_data |
15.851s |
155 / 129 = 26 |
secs: 1670362242 |
secs: 1670362240 |
2601.33 ms |
laptop1_core1/half_data |
22.714s |
224 / 211 = 13 |
secs: 1670361860 |
secs: 1670361858 |
1301.35 ms |
laptop1_core1/quarter_data |
15.9s |
182 / 181 = 1 |
secs: 1670362083 |
secs: 1670362082 |
101.33 ms |
laptop1_core1/quarter_data1 |
15.82s |
155 / 152 = 3 |
secs: 1670362606 |
secs: 1670362605 |
301.33 ms |
laptop1_core1/quarter_data2 |
24.336s |
240 / 227 = 13 |
secs: 1670362742 |
secs: 1670362741 |
1301.35 ms |
laptop1_core1/quarter_data3 |
15.66s |
154 / 152 = 2 |
secs: 1670362923 |
secs: 1670362923 |
101.34 ms |
Experiment 2
Goal:
In the real scenarios, if we send both raw point cloud data and scan data(or late fusion data), we would like to know what will happen.
Results
Note
To make experiment 2 more obvious, in the full_data1 and later tests, I put the router further away from both devices.
exp_name |
t_total |
data_num(new/rs) |
time_new |
time_rs |
t_diff |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
laptop1_core1_exp2 |
13.549 s |
134 / 134 |
secs: 1670377104 |
secs: 1670377104 |
201.356 ms |
laptop1_core1_exp2 |
16.29 s |
163 / 162 |
secs: 1670378257 |
secs: 1670378256 |
101.37 ms |
laptop1_core1_exp2 |
16.29 s |
164 / 162 |
secs: 1670378257 |
secs: 1670378256 |
101.37 ms |
laptop1_core1_exp2 |
11.5s |
115 / 113 |
secs: 1670380380 |
secs: 1670380380 |
1.366 ms |
laptop1_core1_exp2 |
11.5s |
115 / 109 |
secs: 1670380380 |
secs: 1670380379 |
601.36 ms |
laptop1_core1_exp2 |
17.336 s |
170 / 170 |
secs: 1670381602 |
secs: 1670381601 |
1.364 ms |
laptop1_core1_exp2 |
17.336 s |
172 / 139 |
secs: 1670381602 |
secs: 1670381601 |
101.36 ms |
laptop1_core1_exp2 |
16.669s |
162 / 161 |
secs: 1670393027 |
secs: 1670393026 |
201.34 ms |
laptop1_core1_exp2 |
16.669s |
164 / 129 |
secs: 1670393027 |
secs: 1670393025 |
1601.35ms |
Conclusion:
The raw
point clouddata will have more time delay than singlescandata, see thet_diffThe raw
point clouddata will have more package drop than singlescandata, see thedata_num
A wired result when I was analyzing /full_data/scan and /full_data/rs_points:
exp_name |
t_total |
data_num(new/rs) |
time_new |
time_rs |
t_diff |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
laptop1_core1_exp2 |
18.4s |
185 / 184 |
secs: 1670378175 |
secs: 1670378175 |
101.37 ms |
laptop1_core1_exp2 |
18.6s |
186 / 182 |
secs: 1670378175 |
secs: 1670378175 |
1.36 ms |
My analysis for this results are:
Since the scan and rs_point are conducted separately, maybe the network time delay at that time was small, the network situation was good.
Therefore, we need to get both the scan and rs_points data at the same time. This is also why in my following tests:
full_data1 andfull_data2, I made modification like above note.
7 Lidar Rotation drift
Running the lidar for 10 mins, randomly select 5 scan time and plot out the start location of that scan, all look like this:
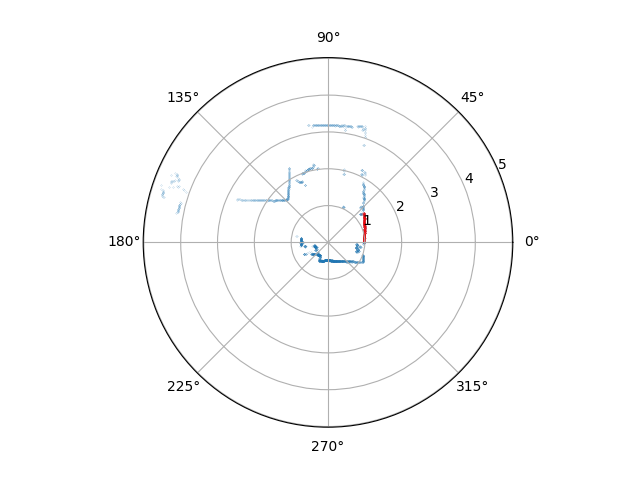
Conclusion: Given the phase lock using PPS from GPS, the Lidar phase is locked and the start point is no longer shifted over time.
Some commands
rostopic echo /new/rslidar_points/header | tee new_header.txt
rostopic echo /rslidar_points/header | tee rs_header.txt
rostopic echo /rslidar_laserscan_new/header | tee new_scan_header.txt
rostopic echo /rslidar_laserscan/header | tee scan_header.txt
rostopic echo /syn_pc_new/header | tee syn_new.txt
rostopic echo /syn_pc_rs/header | tee syn_rs.txt
rosbag record /rslidar_laserscan_new /rslidar_laserscan
rosbag record /new/rslidar_points /rslidar_points
rosbag record /rslidar_laserscan_new /rslidar_laserscan /new/rslidar_points /rslidar_points